Definition of IoT
In the realm of technological advancement, the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that can communicate and exchange data without human intervention. These devices, equipped with sensors and actuators, are capable of collecting and transmitting data over the internet, enabling seamless integration and automation of various processes.
Significance of Genesis in Technology
Genesis represents the inception or origin of something new and innovative. In the context of technology, Genesis symbolizes the beginning of groundbreaking advancements and paradigm shifts. As such, IoT in Genesis signifies the emergence of a new era in technological evolution, characterized by interconnectedness, data-driven insights, and transformative applications.
Understanding IoT Technology
Definition and Components
At its core, IoT technology comprises interconnected devices, sensors, actuators, and communication networks. These components work together to enable the collection, transmission, and analysis of data from the physical world, facilitating automation, optimization, and decision-making in various domains.
Evolution of IoT
The evolution of IoT technology traces back to the convergence of computing, networking, and sensor technologies. From its origins in industrial automation and machine-to-machine communication, IoT has evolved to encompass a wide range of applications across industries such as healthcare, agriculture, transportation, and smart cities.
The Concept of Genesis
Introduction to Genesis
In the context of IoT, Genesis represents the foundational principles and concepts underlying the integration of IoT technologies into diverse environments and applications. It embodies the notion of innovation, transformation, and progress driven by the adoption of IoT solutions.
Genesis as a Conceptual Framework
As a conceptual framework, Genesis provides a roadmap for organizations and individuals seeking to harness the potential of IoT technologies. It encompasses the exploration of new ideas, the development of innovative solutions, and the realization of transformative outcomes through the deployment of IoT-enabled systems and services.
Integration of IoT in Genesis
Adoption of IoT in Genesis
The integration of IoT in Genesis involves the widespread adoption of IoT technologies across various sectors and industries. Organizations, governments, and individuals are increasingly embracing IoT solutions to address challenges, optimize processes, and enhance productivity and quality of life.
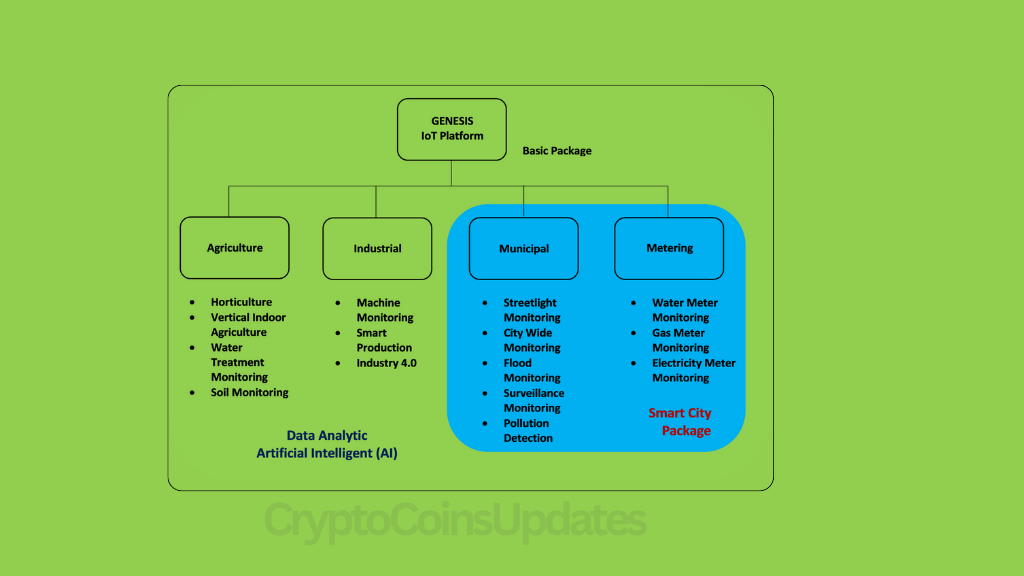
Applications of IoT in Genesis
The applications of IoT in Genesis are diverse and multifaceted, spanning sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, smart cities, and environmental monitoring. From remote patient monitoring and precision agriculture to smart transportation systems and air quality monitoring, IoT is revolutionizing how we interact with and manage the world around us.
IoT Sensors in Genesis
Role of Sensors
Sensors are the backbone of IoT systems in Genesis, playing a crucial role in collecting data from the physical environment. These devices detect and measure various parameters such as temperature, humidity, pressure, and motion, converting physical phenomena into digital signals that can be processed and analyzed.
Types of Sensors Used
There is a wide array of sensors used in Genesis, each tailored to specific applications and environments. Temperature sensors, humidity sensors, pressure sensors, and motion sensors are just a few examples of the diverse range of sensors employed in IoT deployments. These sensors utilize different technologies and sensing principles to accurately capture and quantify data.
Data Collection and Analysis
Importance of Data Collection
Data collection is fundamental to IoT in Genesis, providing the raw material for generating insights and driving decision-making. By collecting data from sensors and devices deployed in the field, organizations can gain visibility into processes, identify patterns, and detect anomalies in real-time.
Analytical Techniques Employed
In addition to data collection, data analysis is essential for extracting value from IoT-generated data. Analytical techniques such as descriptive analytics, diagnostic analytics, predictive analytics, and prescriptive analytics are employed to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations within the data, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and take proactive actions.
IoT Devices in Genesis
Types of Devices Utilized
IoT devices in Genesis encompass a wide range of hardware components, including sensors, actuators, gateways, and edge devices. These devices are designed to collect, transmit, and process data, enabling seamless communication and interaction within IoT ecosystems.
Functions and Capabilities
IoT devices in Genesis are equipped with various functions and capabilities to fulfill their intended roles within IoT systems. From onboard processing and wireless connectivity to power-efficient designs and ruggedized enclosures, these devices are engineered to withstand diverse environmental conditions and deliver reliable performance.
Smart Cities and IoT Integration
Genesis and Smart City Initiatives
The integration of IoT in Genesis has significant implications for smart city initiatives, as it enables the development of connected and sustainable urban environments. Smart cities leverage IoT technologies to optimize resource utilization, enhance public services, and improve quality of life for residents.
Impact of IoT on Urban Development
Through the deployment of IoT sensors, smart meters, and intelligent infrastructure, cities can monitor and manage critical systems such as transportation, energy, water, waste management, and public safety more efficiently and effectively. This leads to improved urban planning, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced livability for citizens.
IoT in Agricultural Genesis
Precision Agriculture Techniques
In agricultural Genesis, IoT plays a pivotal role in enabling precision farming techniques aimed at optimizing crop yields, minimizing resource inputs, and reducing environmental impact. IoT sensors deployed in fields collect data on soil moisture levels, temperature, humidity, and nutrient content, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest management.
Enhancing Crop Yield and Quality
By leveraging IoT-enabled precision agriculture solutions, farmers can achieve greater efficiency, productivity, and sustainability in their operations. Real-time monitoring of environmental conditions and crop health enables timely interventions and adjustments to optimize growing conditions and mitigate risks such as disease outbreaks, pest infestations, and adverse weather events.
Industrial Applications of IoT in Genesis
IoT in Manufacturing Processes
In the industrial domain of Genesis, IoT technologies are revolutionizing manufacturing processes, driving efficiency, agility, and competitiveness. IoT-enabled smart factories leverage interconnected sensors, actuators, and machinery to enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and adaptive production workflows.
Improving Efficiency and Productivity
By integrating IoT into manufacturing processes, organizations can optimize asset utilization, minimize downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and improve product quality and consistency. This leads to enhanced operational efficiency, increased productivity, and greater agility in responding to market demands.
Healthcare and IoT Integration
Remote Patient Monitoring
In healthcare Genesis, IoT technologies facilitate remote patient monitoring solutions that enable healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients’ vital signs, health metrics, and medication adherence outside of traditional clinical settings. IoT-enabled wearable devices, sensors, and mobile health applications collect and transmit real-time health data to healthcare professionals, allowing for early detection of health issues, personalized interventions, and proactive management of chronic conditions.
Healthcare Data Management
IoT integration in healthcare Genesis extends beyond patient monitoring to encompass healthcare data management and analytics. By aggregating and analyzing data from various sources, including electronic health records, medical devices, and population health data, healthcare organizations can gain valuable insights into patient populations, disease trends, and treatment outcomes. Advanced analytics techniques such as predictive modeling, machine learning, and artificial intelligence enable healthcare providers to identify patterns, predict risks, and tailor interventions to individual patient needs, ultimately leading to more effective and personalized care delivery.
IoT Security in Genesis
Ensuring Data Privacy
Security is a paramount concern in Genesis, especially when it comes to IoT deployments. Ensuring data privacy is essential to protect sensitive information collected and transmitted by IoT devices. Robust encryption, authentication mechanisms, and access controls are employed to safeguard data privacy and prevent unauthorized access or tampering. Additionally, organizations implement data protection policies and compliance frameworks to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements and industry standards, thereby mitigating the risk of data breaches and maintaining trust and confidence in IoT systems.
Preventing Cybersecurity Threats
In addition to data privacy, cybersecurity threats pose significant risks to IoT deployments in Genesis. Vulnerabilities in IoT devices, networks, and applications can be exploited by malicious actors to launch cyberattacks such as DDoS attacks, ransomware, and device hijacking. To mitigate cybersecurity threats, organizations implement robust security measures such as network segmentation, intrusion detection systems, firmware updates, and vulnerability management programs. Regular security audits and penetration testing are conducted to identify and address potential weaknesses in IoT systems, ensuring resilience and protection against cyber threats.
Environmental Monitoring with IoT
Monitoring Air and Water Quality
Environmental monitoring is a critical application of IoT in Genesis, enabling the continuous monitoring of air and water quality to safeguard public health and environmental sustainability. IoT sensors deployed in urban and rural areas collect data on pollutants, particulate matter, and chemical contaminants, providing real-time insights into environmental conditions and trends.
Addressing Environmental Challenges
IoT-driven environmental monitoring initiatives in Genesis play a vital role in addressing pressing environmental challenges such as pollution, climate change, and resource depletion. By harnessing real-time data and analytics, policymakers, scientists, and environmental organizations can develop evidence-based strategies and policies to mitigate environmental impacts, promote sustainability, and foster resilience in the face of environmental threats. Furthermore, IoT technologies enable citizen engagement and empowerment, empowering individuals and communities to participate in environmental monitoring efforts, advocate for environmental protection, and contribute to collective efforts to address global environmental challenges in Genesis.
Challenges and Limitations of IoT in Genesis
Connectivity Issues
Connectivity issues pose a significant challenge to IoT deployments in Genesis, particularly in remote or rural areas with limited infrastructure. Inadequate network coverage, bandwidth constraints, and signal interference can hinder the reliable transmission of data between IoT devices and cloud-based platforms, leading to data latency, packet loss, and connectivity disruptions. To address connectivity challenges, organizations may implement alternative communication technologies such as satellite, mesh networks, or low-power wide-area networks (LPWANs) to extend connectivity coverage and ensure seamless communication between IoT devices in Genesis.
Data Privacy Concerns
Data privacy concerns represent another challenge of IoT integration in Genesis, as the collection and processing of vast amounts of sensitive data raise privacy implications for individuals and organizations. Issues such as unauthorized data access, data breaches, and data misuse can compromise privacy rights and erode trust in IoT systems. To mitigate data privacy risks, organizations must implement robust data protection measures, including encryption, anonymization, and access controls, to safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance
Legal Considerations
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in governing IoT deployments in Genesis, providing guidelines, standards, and requirements for ensuring the security, privacy, and interoperability of IoT systems. Regulatory bodies and government agencies establish laws and regulations to address concerns related to data protection, cybersecurity, consumer safety, and environmental impact. Compliance with regulatory requirements is essential for organizations to avoid legal liabilities, penalties, and reputational damage, while also promoting trust and confidence in IoT solutions deployed in Genesis.
Compliance with Industry Standards
In addition to regulatory compliance, adherence to industry standards is essential for ensuring the quality, reliability, and interoperability of IoT solutions in Genesis. Industry standards organizations such as the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) develop standards and protocols to facilitate seamless integration and compatibility between IoT devices and systems. By complying with industry standards, organizations can ensure the compatibility, interoperability, and security of IoT deployments in Genesis, enabling seamless communication and collaboration across heterogeneous environments and ecosystems.